|
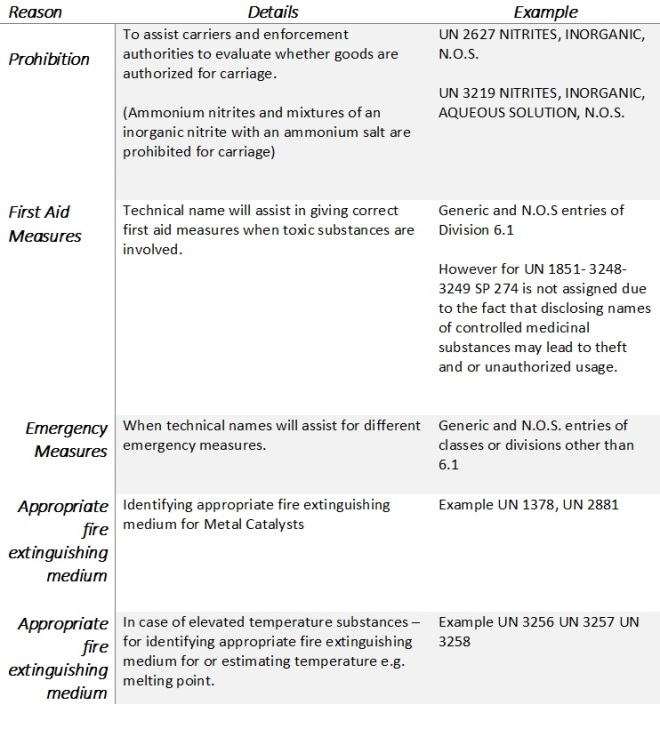
ACIDS
|
ALKALIS
|
|
UN No.
|
Proper Shipping Name
|
UN No.
|
Proper Shipping Name
|
|
1052
|
Hydrogen fluoride, anhydrous* |
1005
|
Ammonia, anhydrous |
|
1182
|
Ethyl chloroformate |
1160
|
Dimethylamine, aqueous solution |
|
1183
|
Ethyldichlorosilane |
1163
|
Dimethylhydrazine, unsymmetrical |
|
1238
|
Methyl chloroformate |
1235
|
Methylamine, aqueous solution |
|
1242
|
Methyldichlorosilane |
1244
|
Methylhydrazine |
|
1250
|
Methyltrichlorosilane |
1382
|
Potassium sulphide, anhydrous or potassium sulphide with less than 30% water of crystallization |
|
1295
|
Trichlorosilane |
1385
|
Sodium sulphide, anhydrous or sodium sulphide with less than 30% water of crystallization |
|
1298
|
Trimethylchlorosilane |
1604
|
Ethylenediamine |
|
1305
|
Vinyltrichlorosilane |
1719
|
Caustic alkali liquid, n.o.s |
|
1572
|
Cacodylic acid |
1813
|
Potassium hydroxide, solid |
|
1595
|
Dimethyl sulphate |
1814
|
Potassium hydroxide, solution |
|
1715
|
Acetic anhydride |
1819
|
Sodium aluminate solution |
|
1716
|
Acetyl bromide |
1823
|
Sodium hydroxide, solid |
|
1717
|
Acetyl chloride |
1824
|
Sodium hydroxide solution |
|
1718
|
Butyl acid phosphate |
1825
|
Sodium monoxide |
|
1722
|
Allyl chloroformate |
1835
|
Tetramethylammonium hydroxide solution |
|
1723
|
Allyl iodide |
1847
|
Potassium sulphide, hydrated with not less than 30% water of crystallization |
|
1724
|
Allyltrichlorosilane, stabilized |
1849
|
Sodium sulphide, hydrated with not less than 30% water |
|
1725
|
Aluminium bromide, anhydrous |
1907
|
Soda lime with more than 4% sodium hydroxide |
|
1726
|
Aluminium chloride, anhydrous |
1922
|
Pyrrolidine |
|
1727
|
Ammonium hydrogendifluoride, solid |
2029
|
Hydrazine, anhydrous |
|
1728
|
Amyltrichlorosilane |
2030
|
Hydrazine, aqueous solution with more than 37% hydrazine, by mass |
|
1729
|
Anisoyl chloride |
2033
|
Potassium monoxide |
|
1730
|
Antimony pentachloride, liquid |
2073
|
Ammonia solution relative density less than 0.880 at 15 °C in water, with more than 35% but not more than 50% ammonia |
|
1731
|
Antimony pentachloride solution |
2079
|
Diethylenetriamine |
|
1732
|
Antimony pentafluoride |
2259
|
Triethylenetetramine |
|
1733
|
Antimony trichloride |
2270
|
Ethylamine, aqueous solution, with not less than 50% but not more than 70% ethylamine |
|
1736
|
Benzoyl chloride |
2318
|
Sodium hydrosulphide with less than 25% water of crystallization |
|
1737
|
Benzyl bromide |
2320
|
Tetraethylenepentamine |
|
1738
|
Benzyl chloride |
2379
|
1,3-Diemthylbutylamine |
|
1739
|
Benzyl chloroformate |
2382
|
Dimethylhydrazine, symmetrical |
|
1740
|
Hydrogendifluorides, n.o.s. |
2386
|
1-Ethylpiperidine |
|
1742
|
Boron trifluoride acetic acid complex, liquid |
2399
|
1-Methylpiperidine |
|
1743
|
Boron trifluoride propionic acid complex, liquid |
2401
|
Piperidine |
|
1744
|
Bromine or bromine solution |
2491
|
Ethanolamine or ethanolamine solution |
|
1745
|
Bromine pentafluoride |
2579
|
Piperazine |
|
1746
|
Bromide trifluoride |
2671
|
Aminopyridines |
|
1747
|
Butyltrichlorosilane |
2672
|
Ammonia solution relative density between 0.880 and 0.957 at 15 °C in water, with more than 10% but not more than 35% ammonia, by mass |
|
1750
|
Chloroacetic acid solution |
2677
|
Rubidium hydroxide solution |
|
1751
|
Chloroacetic acid, solid |
2678
|
Rubidium hydroxide, solid |
|
1752
|
Chloroacetyl chloride |
2679
|
Lithium hydroxide solution |
|
1753
|
Chlorophenyltrichlorosilane |
2680
|
Lithium hydroxide |
|
1754
|
Chlorosulphonic acid (with or without sulphur trioxide) |
2681
|
Caesium hydroxide solution |
|
1755
|
Chromic acid solution |
2682
|
Caesium hydroxide |
|
1756
|
Chromic fluoride, solid |
2683
|
Ammonium sulphide solution |
|
1757
|
Chromic fluoride solution |
2733
|
Amines, flammable, corrosive, n.o.s. or polyamines, flammable, corrosive,n.o.s |
|
1758
|
Chromium oxychloride |
2734
|
Amines, liquid, corrosive, flammable, n.o.s. or polyamines, liquid, corrosive, flammable, n.o.s. |
|
1762
|
Cyclohexenyltrichlorosilane |
2735
|
Amines, liquid, corrosive, n.o.s. or polyamines, liquid, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
1763
|
Cyclohexyltrichlorosilane |
2795
|
Batteries, wet, filled with alkali electric storage |
|
1764
|
Dichloroacetic acid |
2797
|
Battery fluid, alkali |
|
1765
|
Dichloroacetyl chloride |
2818
|
Ammonium polysulphide solution |
|
1766
|
Dichlorophenyltrichlorosilane |
2949
|
Sodium hydrosuonlphide, solid with not less than 25% water of crystallizati |
|
1767
|
Diethyldichlorosilane |
3028
|
Batteries, dry, containing potassium hydroxide, solid electric storage |
|
1768
|
Difluorophosphoric acid, anhydrous |
3073
|
Vinylpyridines, stabilized |
|
1769
|
Diphenyldichlorosilane |
3253
|
Disodium trioxosilicate |
|
1770
|
Diphenyl methylbromide |
3259
|
Amines, solid, corrosive, n.o.s. or polyamines, solid, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
1771
|
Dodecyltrichlorosilane |
3262
|
Corrosive solid, basic, inorganic, n.o.s |
|
1773
|
Ferric chloride, anhydrous |
3263
|
Corrosive solid, basic, organic, n.o.s |
|
1775
|
Fluoroboric acid |
3266
|
Corrosive liquid, basic, inorganic, n.o.s |
|
1776
|
Fluorophosphoric acid, anhydrous |
3267
|
Corrosive liquid, basic, organic, n.o.s |
|
1777
|
Fluorosulphonic acid* |
3293
|
Hydrazine, aqueous solution with not more than 37% hydrazine, by mass |
|
1778
|
Fluorosilicic acid |
3318
|
Ammonia solution relative density less than 0.880 at 15 °C in water, with more than 50% ammonia |
|
1779
|
Formic acid with more than 85% acid by mass |
3320
|
Sodium borohydride and sodium hydroxide solution with not more than 12% sodium borohydride and not more than 40% sodium hydroxide, by mass |
|
1780
|
Fumaryl chloride |
3423
|
Tetramethylammonium hydroxide, solid |
|
1781
|
Hexadecyltrichlorosilane |
3484
|
Hydrazine aqueous solution, flammable, with more than 37% hydrazine, by mass |
|
1782
|
Hexafluorophosphoric acid |
|
|
|
1784
|
Hexyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1786
|
Hydrofluoric acid and sulphuric acid mixture* |
|
|
|
1787
|
Hydriodic acid* |
|
|
|
1788
|
Hydrobromic acid* |
|
|
|
1789
|
Hydrochloric acid* |
|
|
|
1790
|
Hydrofluoric acid* |
|
|
|
1792
|
Iodine monochloride |
|
|
|
1793
|
Isopropyl acid phosphate |
|
|
|
1794
|
Lead sulphate with more than 3% free acid |
|
|
|
1796
|
Nitrating acid mixture* |
|
|
|
1798
|
Nitrohydrochloric acid* |
|
|
|
1799
|
Nonyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1800
|
Octadecyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1801
|
Octyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1802
|
Perchloric acid with not more than 50% acid, by mass* |
|
|
|
1803
|
Phenolsulphonic acid, liquid |
|
|
|
1804
|
Phenyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1805
|
Phosphoric acid, solution |
|
|
|
1806
|
Phosphorus pentachloride |
|
|
|
1807
|
Phosphorus pentoxide |
|
|
|
1808
|
Phosphorus tribromide |
|
|
|
1809
|
Phosphorus trichloride |
|
|
|
1810
|
Phosphorus oxychloride |
|
|
|
1811
|
Potassium hydrogendifluoride, solid |
|
|
|
1815
|
Propionyl chloride |
|
|
|
1816
|
Propyltrichlorosilane |
|
|
|
1817
|
Pyrosulphuryl chloride |
|
|
|
1818
|
Silicon tetrachloride |
|
|
|
1826
|
Nitrating acid mixture, spent* |
|
|
|
1827
|
Stannic chloride, anhydrous |
|
|
|
1828
|
Sulphur chlorides |
|
|
|
1829
|
Sulphur trioxide, inhibited or sulphur trioxide, stabilized |
|
|
|
1830
|
Sulphuric acid with more than 51% acid* |
|
|
|
1831
|
Sulphuric acid, fuming* |
|
|
|
1832
|
Sulphuric acid, spent* |
|
|
|
1833
|
Sulphurous acid |
|
|
|
1834
|
Sulphuryl chloride |
|
|
|
1836
|
Thionyl chloride |
|
|
|
1837
|
Thiophosphoryl chloride |
|
|
|
1838
|
Titanium tetrachloride |
|
|
|
1839
|
Trichloroacetic acid |
|
|
|
1840
|
Zinc chloride solution |
|
|
|
1848
|
Propionic acid with not less than 10% and less than 90% by mass |
|
|
|
1873
|
Perchloric acid with more than 50% but not more than 72% acid, by mass* |
|
|
|
1898
|
Acetyl iodide |
|
|
|
1902
|
Diisooctyl acid phosphate |
|
|
|
1905
|
Selenic acid |
|
|
|
1906
|
Sludge acid* |
|
|
|
1938
|
Bromoacetic acid solution |
|
|
|
1939
|
Phosphorus oxybromide |
|
|
|
1940
|
Thioglycolic acid |
|
|
|
2031
|
Nitric acid, other than red fuming* |
|
|
|
2032
|
Nitric acid, red fuming* |
|
|
|
2214
|
Phthalic anhydride with more than 0.05% of maleic anhydride |
|
|
|
2215
|
Maleic anhydride |
|
|
|
2218
|
Acrylic acid, inhibited |
|
|
|
2225
|
Benzenesulphonyl chloride |
|
|
|
2226
|
Benzotrichloride |
|
|
|
2240
|
Chromosulphuric acid* |
|
|
|
2262
|
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride |
|
|
|
2267
|
Dimethyl thiophosphoryl chloride |
|
|
|
2305
|
Nitrobenzenesulphonic acid |
|
|
|
2308
|
Nitrosylsulphuric acid, liquid* |
|
|
|
2331
|
Zinc chloride, anhydrous |
|
|
|
2353
|
Butyryl chloride |
|
|
|
2395
|
Isobutyrylchloride |
|
|
|
2407
|
Isopropyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2434
|
Dibenzyldichlorosilane |
|
|
|
2435
|
Ethylphenyldichlorosilane |
|
|
|
2437
|
Methylphenyldichlorosilane |
|
|
|
2438
|
Trimethylacetyl chloride |
|
|
|
2439
|
Sodium hydrogendifluoride |
|
|
|
2440
|
Stannic chloride pentahydrate |
|
|
|
2442
|
Trichloroacetyl chloride |
|
|
|
2443
|
Vanadium oxytrichloride |
|
|
|
2444
|
Vanadium tetrachloride |
|
|
|
2475
|
Vanadium trichloride |
|
|
|
2495
|
Iodine pentafluoride |
|
|
|
2496
|
Propionic anhydride |
|
|
|
2502
|
Valeryl chloride |
|
|
|
2503
|
Zirconium tetrachloride |
|
|
|
2506
|
Ammonium hydrogen sulphate |
|
|
|
2507
|
Chloroplatinic acid, solid |
|
|
|
2508
|
Molybdenum pentachloride |
|
|
|
2509
|
Potassium hydrogen sulphate |
|
|
|
2511
|
2-Chloropropionic acid |
|
|
|
2513
|
Bromoacetyl bromide |
|
|
|
2531
|
Methacrylic acid, stablilized |
|
|
|
2564
|
Trichloroacetic acid solution |
|
|
|
2571
|
Alkylsulphuric acids |
|
|
|
2576
|
Phosphorus oxybromide, molten |
|
|
|
2577
|
Phenylacetyl chloride |
|
|
|
2578
|
Phosphorus trioxide |
|
|
|
2580
|
Aluminium bromide solution |
|
|
|
2581
|
Aluminium chloride solution |
|
|
|
2582
|
Ferric chloride solution |
|
|
|
2583
|
Alkylsulphonic acids, solid or arylsulphonic acids, solid with more than 5% free sulphuric acid |
|
|
|
2584
|
Alkylsulphonic acids, liquid or arylsulphonic acids, liquid with more than 5% free sulphuric acid |
|
|
|
2585
|
Alkylsulphonic acids, solid or arylsulphonic acids, solid with not more than 5% free sulphuric acid |
|
|
|
2586
|
Alkylsulphonic acids, liquid or arylsulphonic acids, liquid with not more than 5% free sulphuric acid |
|
|
|
2604
|
Boron trifluoride diethyl etherate |
|
|
|
2626
|
Chloric acid, aqueous solution with not more than 10% chloric acid |
|
|
|
2642
|
Fluoroacetic acid |
|
|
|
2670
|
Cyanuric chloride |
|
|
|
2691
|
Phosphorus pentabromide |
|
|
|
2692
|
Boron tribromide |
|
|
|
2698
|
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydrides with more than 0.05 % of maleic anhydride |
|
|
|
2699
|
Trifluoroacetic acid |
|
|
|
2739
|
Butyric anhydride |
|
|
|
2740
|
n-Propyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2742
|
Chloroformates, toxic, corrosive, flammable, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
2743
|
n-Butyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2744
|
Cyclobutyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2745
|
Chloromethyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2746
|
Phenyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2748
|
2-Ethylhexyl chloroformate |
|
|
|
2751
|
Diethylthiophosphoryl chloride |
|
|
|
2789
|
Acetic acid, glacial or acetic acid solution, more than 80% acid, by mass |
|
|
|
2790
|
Acetic acid solution, more than 10% but not more than 80% acid, by mass |
|
|
|
2794
|
Batteries, wet filled with acid electric storage |
|
|
|
2796
|
Sulphuric acid with not more than 51% acid or battery fluid, acid* |
|
|
|
2798
|
Phenylphosphorus dichloride |
|
|
|
2799
|
Phenylphosphorus thiodichloride |
|
|
|
2802
|
Copper chloride |
|
|
|
2817
|
Ammonium hydrogendifluoride solution |
|
|
|
2819
|
Amyl acid phosphate |
|
|
|
2820
|
Butyric acid |
|
|
|
2823
|
Crotonic acid, solid |
|
|
|
2826
|
Ethyl chlorothioformate |
|
|
|
2829
|
Caproic acid |
|
|
|
2834
|
Phosphorous acid |
|
|
|
2851
|
Boron trifluoride dehydrate |
|
|
|
2865
|
Hydroxylamine sulphate |
|
|
|
2869
|
Titanium trichloride mixture |
|
|
|
2879
|
Selenium oxychloride |
|
|
|
2967
|
Sulphamic acid |
|
|
|
2985
|
Chlorosilanes, flammable, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
2986
|
Chlorosilanes, corrosive, flammable, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
2987
|
Chlorosilanes, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
2988
|
Chlorosilanes, water-reactive, flammable, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3246
|
Methanesulphonyl chloride |
|
|
|
3250
|
Chloroacetic acid, molten |
|
|
|
3260
|
Corrosive solid, acidic, inorganic, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3261
|
Corrosive solid, acidic, organic, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3264
|
Corrosive liquid, acidic, inorganic, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3265
|
Corrosive liquid, acidic, organic, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3277
|
Chloroformates, toxic, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3361
|
Chlorosilanes, toxic, corrosive, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3362
|
Chlorosilanes, toxic, corrosive, flammable, n.o.s. |
|
|
|
3412
|
Formic acid with not less than 10% but not more than 85% acid by mass |
|
|
|
3412
|
Formic acid with not less than 5% but not more than 10% acid by mass |
|
|
|
3419
|
Boron trifluoride acetic acid complex, solid |
|
|
|
3420
|
Boron trifluoride propionic acid complex, solid |
|
|
|
3421
|
Potassium hydrogendifluoride solution |
|
|
|
3425
|
Bromoacetic acid, solid |
|
|
|
3453
|
Phosphoric acid, solid |
|
|
|
3456
|
Nitrosylsulphuric acid, solid |
|
|
|
3463
|
Propionic acid with not less than 90% acid by mass |
|
|
|
3472
|
Crotonic acid, liquid |
|
|